Climate measures for the food industry
Reducing carbon dioxide emissions in food production can be done through a combination of measures that are relatively easy to implement. The biggest savings are often linked to the production and handling of the raw material itself, where efficient handling and minimization of food waste has a big effect on emission levels.
What many people miss, however, is that there are many other efforts to be made, not least when it comes to energy efficiency and heat recovery.
Background
Every day, huge amounts of hot air is vented out via industrial & process ventilation from factories. When this air contains dirt, grease, soot or other particles from the process itself, it is impossible and/ or very expensive to use traditional heat exchangers to recover the energy in the air. And, therefore this hot air is instead vented straight out.
Lepido is a Swedish-made liquid-coupled heat exchanger developed specifically for heat recovery in dirty exhaust air, without pre-filtration requirements.

Lepido makes it possible to take advantage of the heat that is currently vented out via industry or process ventilation and return that energy to the process itself, or as heating of the property itself. By reusing the energy from the process, energy use is reduced, which saves money and reduces emissions of fossil CO2.
Food Production
Food production units often have large air flows with high temperature in the process air. In order not to risk costly downtime due to clogging, recycling and reuse of excess heat in the exhaust air is often not carried out. However, if you succeed in recovering this waste heat, it can be returned as a supplement to ventilation, hot water or other process-specific heat-demanding equipments.
The challenge
Recycling of waste heat in food production presents many challenges. The process air
often contains high concentrations of fat, moisture and even dirt particles. The risk of downtime must be minimized while maintenance must not be overly time-consuming or costly. In many production facilities there is also a lack of space, which requires a technical solution with flexible placement and piping.

The image above shows hot air being ventilated straight out into the air without energy recovery as a result of these challenges.
The solution
Lepido is an industrial tube heat exchanger with a patented set up of coils which allows the particles (and the hot air) to pass through the heat exchanger without getting stuck. It can recapture excess heat from dirty ventilation in industrial processes. Lepido has no need for pre-filtration, which minimizes maintenance and diminishes the total pressure drop.
.png?width=1200&height=627&name=Without%20energy%20recovery%20(2).png)
Project data
This data is based on a project delivered in 2022. It is a food production unit, and the recaptured excess heat is returned to the production facility supply air.
Type: Production unit for food production
Airflow: 9,7 m3/s
Air temp: 40°C
Pollutants: Grease, soot & moisture
Return: 9,7 m3/s supply air to production facility
Model: 2 x L50 (1100x1800x900 mm)
Set temperature: +16°C
Need: 355 kW
Operating hours: 20 h/day
Energy need: 616 600 kWh/year
Lepido Heat exchange effect: 288 kW
Energy recovery: 614 900 kWh/year
Installation
In this project, the Lepido was installed as part of the exhaust air duct, where the air stream is heavily contaminated with soot and grease due to the duct serving the high-intensity production line. The recovered heat is fed back to the supply AHU serving the production line via a run-around heat exchange circuit, which means there is no risk of transfer of odours, or of the heat exchangers clogging up with particles.

Results
The recovered excess heat in this project covers 99% of the demand for heat in the production facility. Annual energy savings is 614 900 kWh per year.
The building parameters also allowed the Lepido solution to offer great installation simplifications as the energy recovery functionality could be decentralized from the main technical room – saving vast stretches of both ducting and piping installations. The possibility to place the Lepido close to the actual production line also greatly simplified maintenance, reducing time and cost.
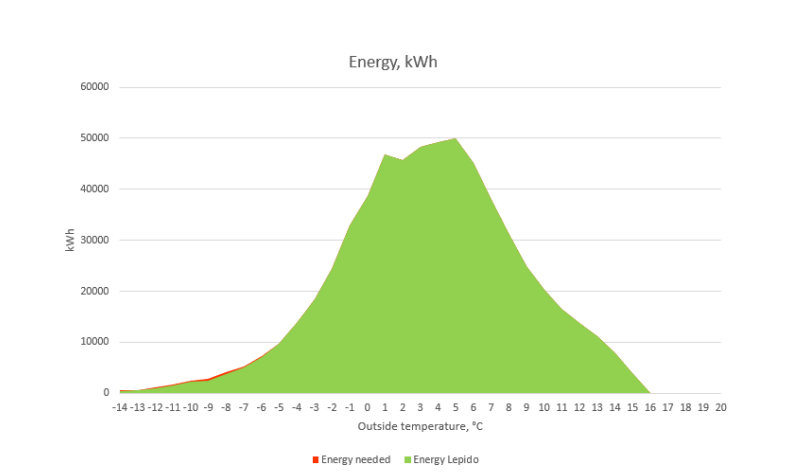
Exhibit : Graph showing the recovered energy in green and the total required energy in red – Lepido covers 99% of the required energy for this site
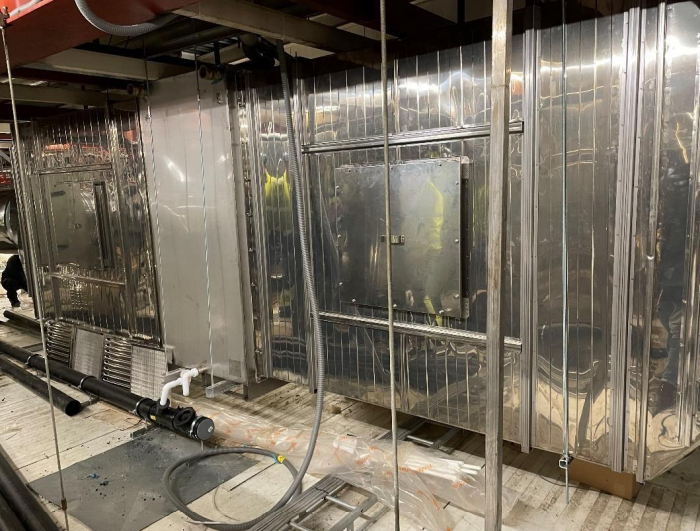

Exhibit: Service hatches installed before and after the heat exchanger
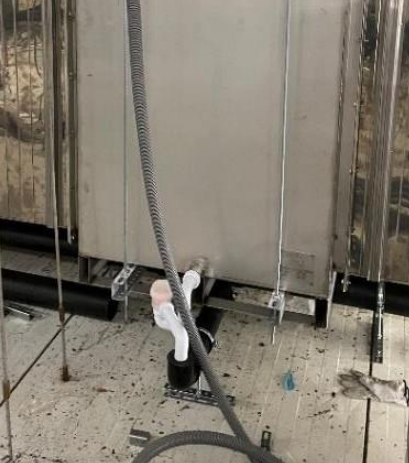

Exhibit: Drain connection, removing water both from condensation during operation and any excess water used during cleaning/maintenance
.png?width=1200&height=627&name=Expand%20your%20operations%20Become%20a%20partner%20(3).png)